Have you ever experienced excruciating period pain that feels like your worst nightmare? Well, you’re not alone. Many women around the world face this challenge every month. But what if we told you that there’s more to this pain than meets the eye? If you are a woman who experiences severe menstrual cramps, heavy bleeding, painful sex, or infertility, you may be suffering from a condition called Endometriosis.
Endometriosis is a disease that affects about 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide, and it can have a significant impact on your physical, mental, and social well-being. But what exactly is Endometriosis and how does it affect your health? In this blog post, we’ll dive into what Endometriosis is and explore its impact on women’s health, what causes it, what are the symptoms and complications, and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
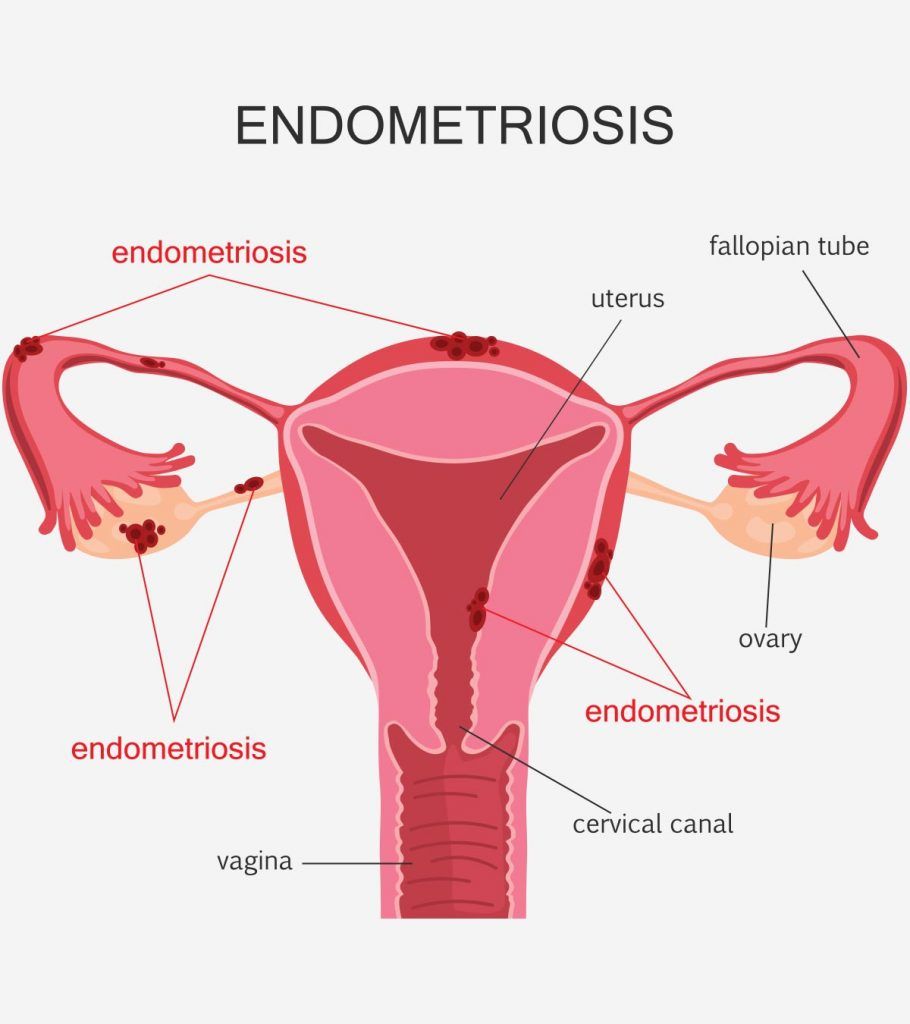
What is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a chronic condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, typically in the pelvic area. It can grow on various organs in the pelvic area, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, bowel, or rectum. In rare cases, it can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or brain. This misplaced tissue continues to act as it would inside the uterus, thickening and breaking down during each menstrual cycle. However, since it’s located outside the uterus, it has no way to exit the body. As a result, it causes inflammation, scarring, and pain.
The ectopic endometrial tissue responds to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, just like the normal endometrium. This means that it thickens, breaks down, and bleeds every month. However, unlike the normal endometrium, which exits the body through the vagina as menstrual blood, the ectopic tissue has no way to escape. This causes inflammation, pain, scarring, and adhesions (abnormal attachments between organs) in the affected areas.
Endometriosis affects approximately 1 in 10 women worldwide, making it a prevalent condition. Unfortunately, it often goes undiagnosed or misdiagnosed for years, with an average delay of 7-10 years in diagnosis. This delay is due to a lack of awareness and the normalization of period pain in society. Women often suffer in silence, believing that severe pain is just a regular part of being a woman. A study conducted in Lagos revealed that 40% of women with infertility issues were diagnosed with Endometriosis. This suggests a significant impact on women’s reproductive health in Nigeria. With increased awareness and access to proper healthcare, we can empower women to seek timely diagnosis and treatment.
On the DRO Health app, you can speak to a General Practitioner or a Gynecologist if you need to speak to a professional about any pains you might be experiencing as a woman. Visit www.drohealth.com for more information on the next steps.
What causes Endometriosis?
The exact cause of Endometriosis is not known, as several factors may contribute to its development. Some of these factors include:
- Retrograde menstruation: This occurs when menstrual blood containing endometrial cells flows back through the fallopian tubes and into the pelvic cavity at the time that blood is flowing out of the body through the cervix and vagina during periods. Retrograde menstruation can result in endometrial-like cells being deposited outside the uterus where they can implant and grow.
2. Cellular metaplasia: This occurs when cells change from one form to another. Cells outside the uterus change into endometrial-like cells and start to grow.
3. Stem cells: These are cells that can give rise to different types of cells in the body. Stem cells may migrate from the bone marrow or other tissues to the pelvic area and differentiate into endometrial-like cells.
4. Genetic factors: Some women may inherit genes that make them more prone to developing endometriosis or having more severe symptoms.
5. Immune system dysfunction: Some women may have an impaired immune system that fails to recognize and eliminate the ectopic endometrial cells or produces inflammatory substances that aggravate the condition.
6. Environmental factors: Some chemicals or toxins in the environment may disrupt the hormonal balance or affect the immune system and increase the risk of Endometriosis.

What are the symptoms and complications of Endometriosis?
The most common symptom of Endometriosis is pain. The pain can vary in intensity, frequency, location, and timing. Some women may experience pain only during their periods (dysmenorrhea), while others may have pain throughout their cycle or even constantly. The pain can affect different body parts depending on where the ectopic tissue is located. Beyond the excruciating menstrual pain, Endometriosis can manifest through a variety of symptoms. For example, some women may have pain in their lower abdomen, pelvis, back, or legs; others may have pain during or after sex (dyspareunia), urination (dysuria), or bowel movements (dyschezia).
Other symptoms of endometriosis may include:
- Chronic pelvic pain: Women with endometriosis often experience persistent pelvic pain that may worsen during menstruation or sexual intercourse.
- Fatigue and low energy levels: The constant pain and inflammation can drain a woman’s energy, affecting her quality of life. Some women may have excessive bleeding during their periods (menorrhagia) or bleeding between periods (metrorrhagia). This can lead to anaemia (low red blood cell count) and fatigue.
- Painful bowel movements and urination: Some women may have endometriosis in their bowel or bladder, which can cause symptoms such as constipation, diarrhoea, bloating, nausea, vomiting, blood in the urine or stool, or urinary tract infections. Endometriosis can cause pain and discomfort during bowel movements and urination, sometimes leading to misdiagnoses like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
- Infertility: Endometriosis is a leading cause of infertility in women, affecting up to 50% of those struggling to conceive. This can be caused by scarring or adhesions that block or damage the fallopian tubes or ovaries; inflammation or hormonal imbalance that affects ovulation or implantation; or immune system dysfunction that interferes with fertilization or embryo development.
- Other complications: In rare cases, endometriosis can cause serious complications such as bowel obstruction, bladder rupture, kidney damage, lung collapse, or brain haemorrhage due to the spread of the ectopic tissue to these organs.
The emotional and psychological toll of endometriosis cannot be overlooked. Coping with chronic pain, fertility concerns, and the impact on relationships can lead to anxiety, depression, and a decreased sense of well-being. It’s crucial to provide emotional support and resources to help women navigate these challenges.
How is Endometriosis diagnosed and treated?
If you suspect you might have endometriosis, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Your doctor will likely begin with a detailed medical history, and physical examination, and may recommend imaging tests or laparoscopy (a minimally invasive surgery) for a definitive diagnosis. Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows the doctor to see and biopsy the ectopic tissue inside the abdomen.
However, laparoscopy is not always available or affordable for many women, especially in low-resource settings. Therefore, some doctors may rely on other methods such as medical history, physical examination, ultrasound, blood tests, or empirical treatment to diagnose or rule out endometriosis.
To book an affordable diagnostic test anywhere in Nigeria, download the DRO Health app here. Book a test on your mobile phone, get your test done at a centre and receive your results within 7 days.
While there is no cure for endometriosis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include pain medications, hormonal therapies, or in severe cases, surgery to remove endometrial tissue. Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual, taking into account factors like pain severity, desire for fertility, and overall health.
The key to overcoming endometriosis lies in raising awareness and breaking the silence. Educating ourselves and others can empower women to seek timely medical intervention, reduce diagnostic delays, and enhance their overall well-being. In Nigeria, organizations like the Endometriosis Support Group Nigeria (ESGN) are actively working to create awareness, provide support, and advocate for better healthcare services for women with Endometriosis.
Our final words to you,
Endometriosis is a common but often misunderstood condition that affects many women around the world. By understanding the symptoms, impact, and available treatment options, we can support women in their journey towards better health and well-being. Together, let’s break the silence, raise awareness, and ensure that no woman suffers in silence. Remember, your pain matters, and you deserve to live a life free from endometriosis.
If you suspect you may have endometriosis or know someone who does, please consult with a doctor or a Gynecologist by visiting our website www.drohealth.com. Our professionals are always ready to speak to you.